As of 2025, global network of Bitcoin ATM continues its expansion, cementing its role as a convenient, albeit often costly, bridge between traditional cash economies and the digital currency world. As of the third quarter of 2025, the number of these crypto kiosks has grown, reflecting a sustained demand for accessible cryptocurrency transactions. This in-depth analysis explores the mechanics, market leaders, costs, and regulatory environment of Bitcoin ATMs, providing a comprehensive overview for researchers and users alike.
How Does a Bitcoin ATM Work?
Contrary to their name, Bitcoin ATMs do not connect to traditional banking networks. Instead, they are internet-connected kiosks that interact directly with blockchain networks and cryptocurrency exchanges. They function as a specialized portal for converting fiat currency into digital currency, and in some cases, vice versa.
The typical user workflow for purchasing Bitcoin involves the following steps:
- Initiation: The user selects the “Buy” option and the specific cryptocurrency desired (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin) on the kiosk’s touchscreen.
- Identity Verification: Depending on the transaction size and jurisdiction, the machine prompts the user for verification. This ranges from entering a mobile phone number for an SMS code to scanning a government-issued ID and undergoing facial recognition analysis.
- Wallet Designation: The user must provide a destination for the cryptocurrency. This is most commonly achieved by presenting a QR code from a mobile wallet app to the ATM’s scanner.
- Payment: The user inserts fiat cash into the bill acceptor or, on some newer models, uses a debit card.
- Execution: Once confirmed, the operator purchases the equivalent amount of crypto (minus fees) and initiates an on-chain transaction to send the assets to the user’s provided wallet address.
What Are the Transaction Limits Imposed on Users?
Transaction limits are not uniform; they are a complex balancing act determined by the operator’s risk appetite and, more importantly, local jurisdictional regulations.
Generally, the industry operates on a tiered system geared toward compliance:
- Low Tier (Unverified/SMS only): Some operators allow small transactions (e.g., $20 to $900) with minimal verification, though this is becoming increasingly rare due to regulatory pressure.
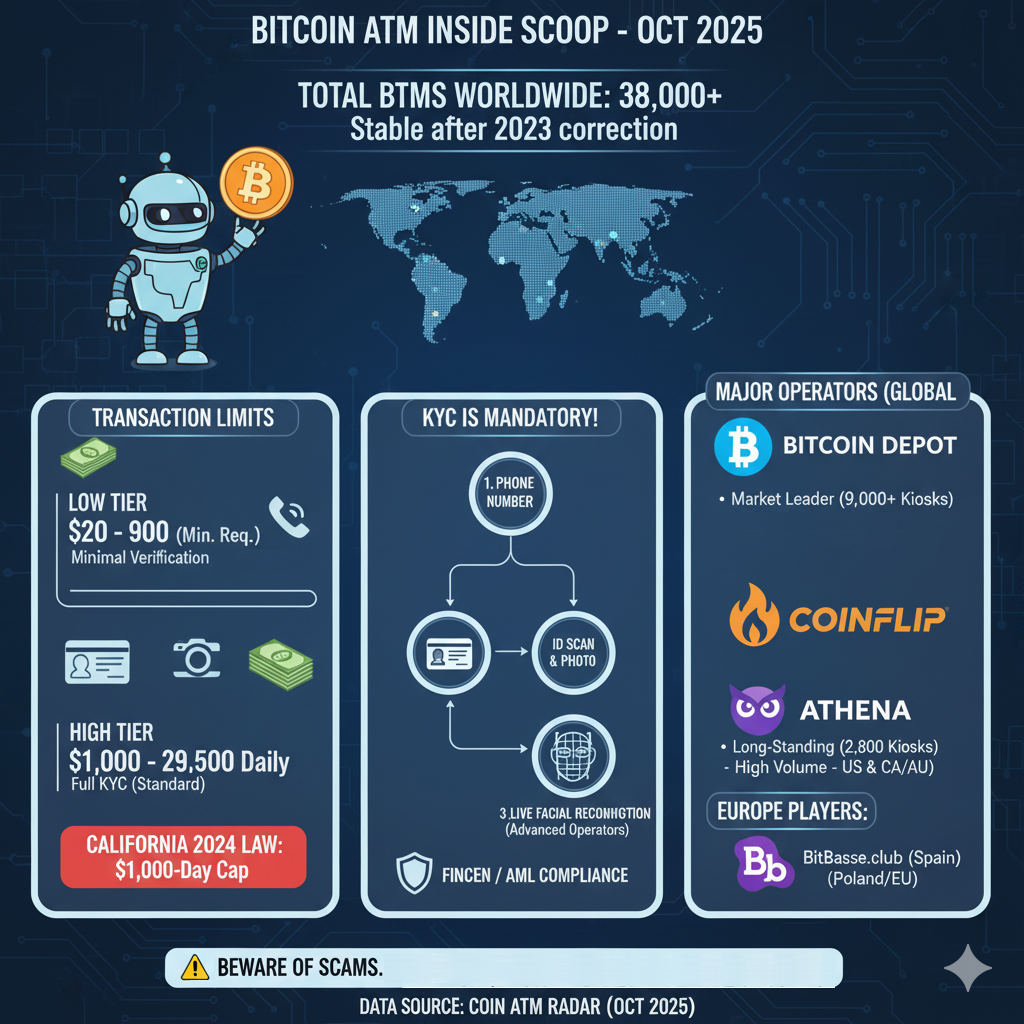
- High Tier (Full KYC): For transactions ranging from $1,000 to nearly $30,000 daily, full identity verification is mandatory.
Regulatory bodies have actively moved to lower these limits to curb financial crime. For instance, specifically in the United States, California implemented legislation effective in 2024 that capped BTM transactions at $1,000 per person, per day, forcing high-volume users toward more regulated exchanges. Users seeking to move large amounts of capital must provide extensive documentation to satisfy Anti-Money Laundering (AML) protocols.

How Many Bitcoin ATMs are There and Which Country Has the Highest Numbers?
According to data maintained by Coin ATM Radar, the definitive industry tracking authority, the global number of installed Bitcoin ATMs has stabilized around the 38,000 to 39,000 mark as of late 2025. After a period of retraction in 2023, the market has found a steady equilibrium.
The geographical distribution is heavily skewed. The United States is the undisputed leader, hosting over 80% of all machines worldwide. This concentration is due to high consumer demand, a relatively established (if complex) regulatory framework, and the presence of the largest manufacturing and operating companies.
Following the U.S., Canada maintains the second-largest network, holding approximately 7.7% of the global share. Australia has emerged as a rapidly growing market, securing the third spot. In Europe, Spain and Poland are the clear leaders in deployment.
What Are the Key Cities with Bitcoin ATMs?
Adoption is highest in densely populated urban centers where the demand for alternative financial services and remittances is greatest.
- United States: Data indicates that Los Angeles, Houston, and Chicago have the highest density of machines, serving as primary hubs for the U.S. market.
- International: Outside North America, Sydney has become a major hub following Australia’s push for adoption. Hong Kong remains a critical access point in Asia, and European capitals with favorable regulations, such as Madrid and Warsaw, host significant numbers of kiosks.
Who Are the Major Companies Offering Bitcoin ATMs and How Many Do They Operate?
The BTM market is an oligopoly dominated by a few large-scale operators who have managed to navigate the high costs of hardware deployment and regulatory compliance. Based on Q2/Q3 2025 operational data and public filings, the major players are:
- Bitcoin Depot: As a publicly traded entity and the market leader in North America, Bitcoin Depot continues to expand its footprint. As of late 2025, the company manages a massive network exceeding 9,000 kiosks. Their strategy focuses heavily on placements in high-traffic retail locations like convenience stores.
- CoinFlip: Recognized for high transaction volumes and a robust customer service infrastructure, CoinFlip operates the second-largest network. Their fleet has surpassed 5,000 machines globally, with a strong presence in the U.S., Canada, and expansion into international markets like Australia and dozens of other countries.
- Athena Bitcoin: A veteran player in the space, Athena Bitcoin maintains a substantial network. Recent reporting places their operational count at approximately 2,800 machines, with a focus regarding both U.S. and Latin American markets.
- International Players: In Europe, BitBase is a dominant force, particularly in Spain, operating over 130 ATMs and physical stores. Shitcoins.club, known for its distinctive branding, operates 329 terminals primarily across the European continent.
What is the Convenience Fee and How Much Does it Cost?
The defining characteristic of Bitcoin ATMs is the high cost of convenience. Unlike online exchanges that benefit from economies of scale, BTM operators must cover costs for physical hardware, armored cash transport, retail rent, and expensive compliance software.
Consequently, fees are substantial. Industry analysis shows that the total markup (the difference between the spot price and the price paid at the machine) typically ranges from 5% to over 20%.
These fees are often split into two parts: a flat transaction fee and a percentage spread hidden in the exchange rate offered by the machine. For example, prominent European operator Kurant has published fee structures indicating markups around 8% for buying and 4% for selling, though these can vary by specific location and machine type. Users are paying a significant premium for the immediacy and cash-based nature of the transaction.
Is Verification and KYC Required to Use a Bitcoin ATM?
Yes. The perception of Bitcoin ATMs as tools for anonymous transactions is outdated and inaccurate in the 2025 landscape. Operators are classified as Money Services Businesses (MSBs) in the U.S. (regulated by FinCEN) and equivalent designations worldwide.
To comply with the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws, virtually all reputable operators enforce Know Your Customer (KYC) processes.
- For the smallest tiers permitted by law, this might only involve SMS verification to link a phone number to a transaction.
- For standard and higher transaction amounts, the machine will require the scanning of a government-issued driver’s license or passport.
- Advanced biometrics, such as facial comparison between the user and their ID, are now standard features on modern machines utilized by major operators like Bitcoin Depot and CoinFlip to prevent identity fraud.
Is a Bitcoin ATM Safe?
Safety must be analyzed from two perspectives: the technical security of the machine and the risk of user-targeted fraud.
Technically, BTMs from established operators are secure. They utilize encrypted connections to process transactions and do not store consumer funds on the machine itself. The blockchain settlement layer is immutable and secure.
However, from a consumer protection standpoint, they carry high risks. Agencies such as the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the FBI have issued numerous warnings regarding the use of Bitcoin ATMs in fraud schemes. Because BTM transactions are instant and irreversible, scammers frequently direct victims (through romance scams, imposter scams, or tech support fraud) to withdraw cash and deposit it into a Bitcoin ATM, sending the funds to the scammer’s wallet. While the machine is working correctly, the user is being defrauded.
Can You Sell Bitcoin at a Bitcoin ATM?
Yes, but not at all locations. The market is divided into “unidirectional” (buy only) and “bidirectional” (buy and sell) machines. Bidirectional machines are more expensive to operate as they require larger cash reserves in the machine to pay out sellers.
To sell Bitcoin at a bidirectional ATM:
- The user selects “Sell” and the amount of cash desired.
- The ATM prints a receipt or displays a QR code representing the operator’s wallet address and the exact amount of crypto required.
- The user sends the crypto from their mobile wallet to the ATM’s address.
- Once the transaction achieves the required number of confirmations on the blockchain (which can take 10 to 60 minutes depending on network congestion), the machine dispenses the cash to the user.
Final Thoughts
Bitcoin ATMs are a permanent part of the crypto world in 2025. They are very convenient if you need to buy crypto quickly with cash.
However, this convenience is expensive. The fees are very high, making them a poor choice for regular investing. They also come with security risks, as they are often used in scams.
The bottom line: Use Bitcoin ATMs carefully and only when you absolutely need to. For most people, using a well-known online exchange is much cheaper and safer.
